|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |
“Mr. Smith, could you explain to us what recursion is all about?” The professor in Introduction to Programming asked an apathetic student. “I don’t know the question, but sex, money, or both is definitely the answer, and God, justice, our values, and love are just the excuses,” I replied. “You shall not pass,” the teacher was far from amused, Apocalypse, Anawim, #justtothepoint.
Parametric curves are mathematical descriptions of curves using one or more parameters. Instead of expressing the relationship between x and y, parametric equations represent x and y (and maybe z) as functions of one or more parameters, often denoted by t, u, or other symbols.
A parametric curve in two dimensions is usually given by the equations: x = x(t), y = y(t), e.g., x = acos(t), y = asin(t). Notice that x2 + y2 = a2cos2(t) + a2sin2(t) = a2, that is, its shape is a circle where t = 0, (x, y) = (acos(0), asin(0)), t = π⁄2, (x, y) = (acos(π⁄2), asin(π⁄2)) = (0, a), and its trajectory is counter-clockwise (Figure 2.f.).
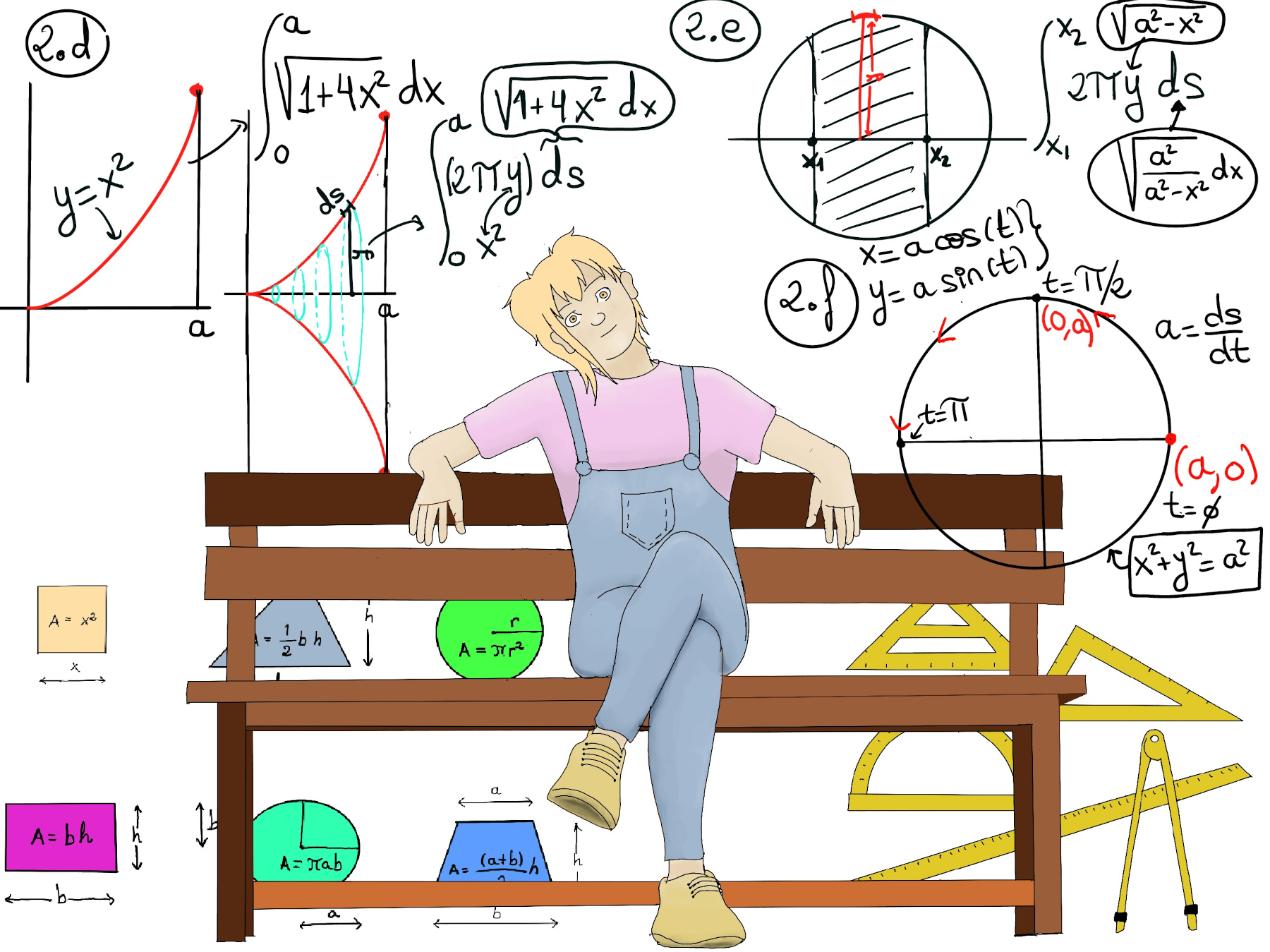
To calculate its arc length, ds2 = dx2 + dy2 ⇒ ds = $\sqrt{(\frac{dx}{dt})^2+(\frac{dy}{dt})^2}dt$, dx/dt = -asin(t), dy/dt = acos(t), ds = $\sqrt{(-asin(t))^2+(acos(t)^2)}dt = \sqrt{a^2}dt = adt,$ and a = ds/dt, that is, the speed or rate of change is a.
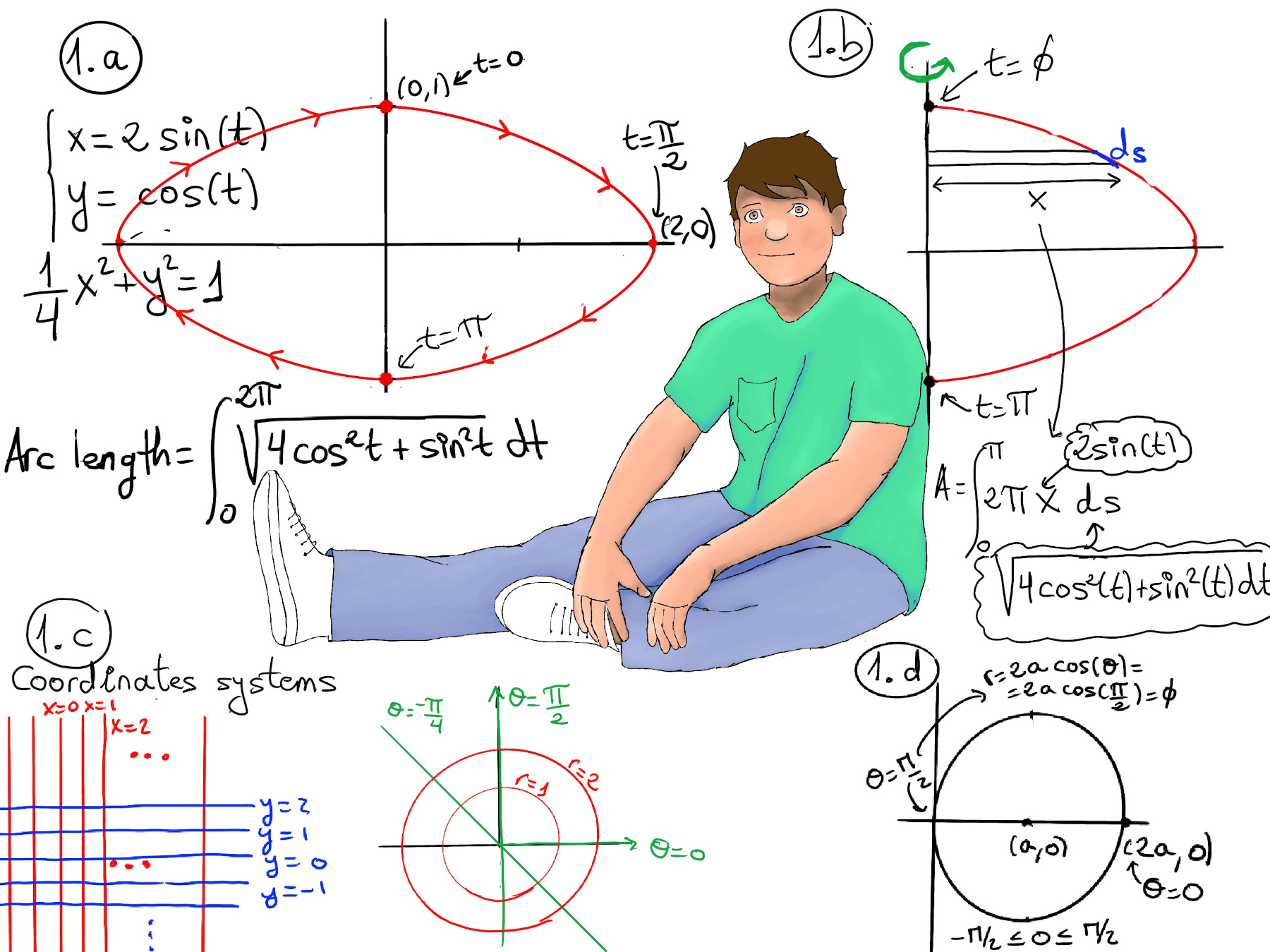
The equation of an ellipse in standard form with its center at the origin (0, 0) is given by: $\frac{x^2}{a^2}+\frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1.$
At t = 0, (2sin(0), cos(0)) = (0, 1). At t = π⁄2, (2sin(π⁄2), cos(π⁄2)) = (2, 0), so its trajectory is clockwise.
$\frac{ds}{dt}Polar Coordinates. = \sqrt{(2cos(t))^2+(sin(t))^2}$. Arc length = $\int_{0}^{2π} \sqrt{(2cos(t))^2+(sin(t))^2}dt = \int_{0}^{2π} \sqrt{4cos^2(t)+sin^2(t)}dt$
An the surface area of the ellipsoid formed by revolving x = 2sin(t), y = cos(t) around the y-axis -Figure 1.b.- = $\int_{0}^{π} 2πxds = \int_{0}^{π} 2π(2sin(t))\sqrt{4cos^2(t)+sin^2(t)}dt$

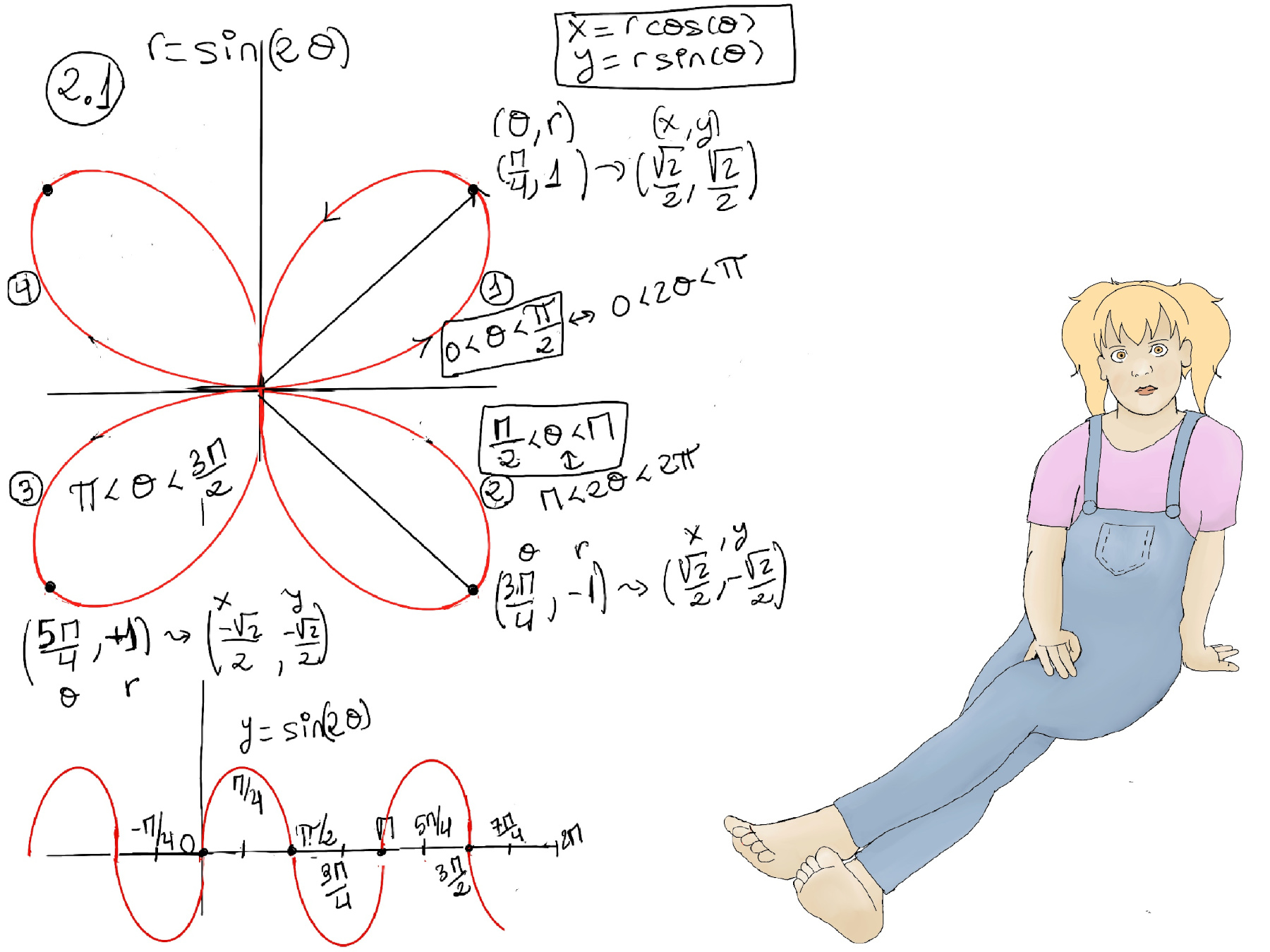
Polar coordinates are an alternative way of specifying the position of a point in a plane using two quantities: the radial distance (r) and the angular coordinate (θ). Instead of using the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), polar coordinates use the pair (r,θ) where r represents the distance from the origin or pole to the point, and θ is the angle formed by the ray from the origin to the point with the horizontal or x-axis, and we typically assume 0 ≤ r < ∞, 0 < θ ≤ 2π.
More formally, x = rcos(θ), y = rsin(θ), r = $\sqrt{x^2+y^2}, θ = tan^{-1}\frac{y}{x}$ (Figure 1.c.), e.g. (x y) = (1, -1), r = $\sqrt{1^2+1^2} = \sqrt{2},θ = arctan(\frac{y}{x}) = arctan(\frac{-1}{1}) = \frac{-π}{4}$ where θ is in the fourth quadrant.
Some typical examples are the circle (r = a), rays (θ = c), and the Archimedean spirar (r = aθ -a spiral with a constant rate of increase in the radial distance -r- as the angle -θ- increases).
How to graph polar coordinates? Let’s plot (3, 45°) -a ray of 45° measured from the x-axis counter-clockwise and the point is going to be in the third circle-, (1, -π⁄4), and (-1⁄2, π⁄3) -Figure 1.a- When graphing a polar coordinate with a negative radius, you move from the pole in the direction opposite the given positive angle.
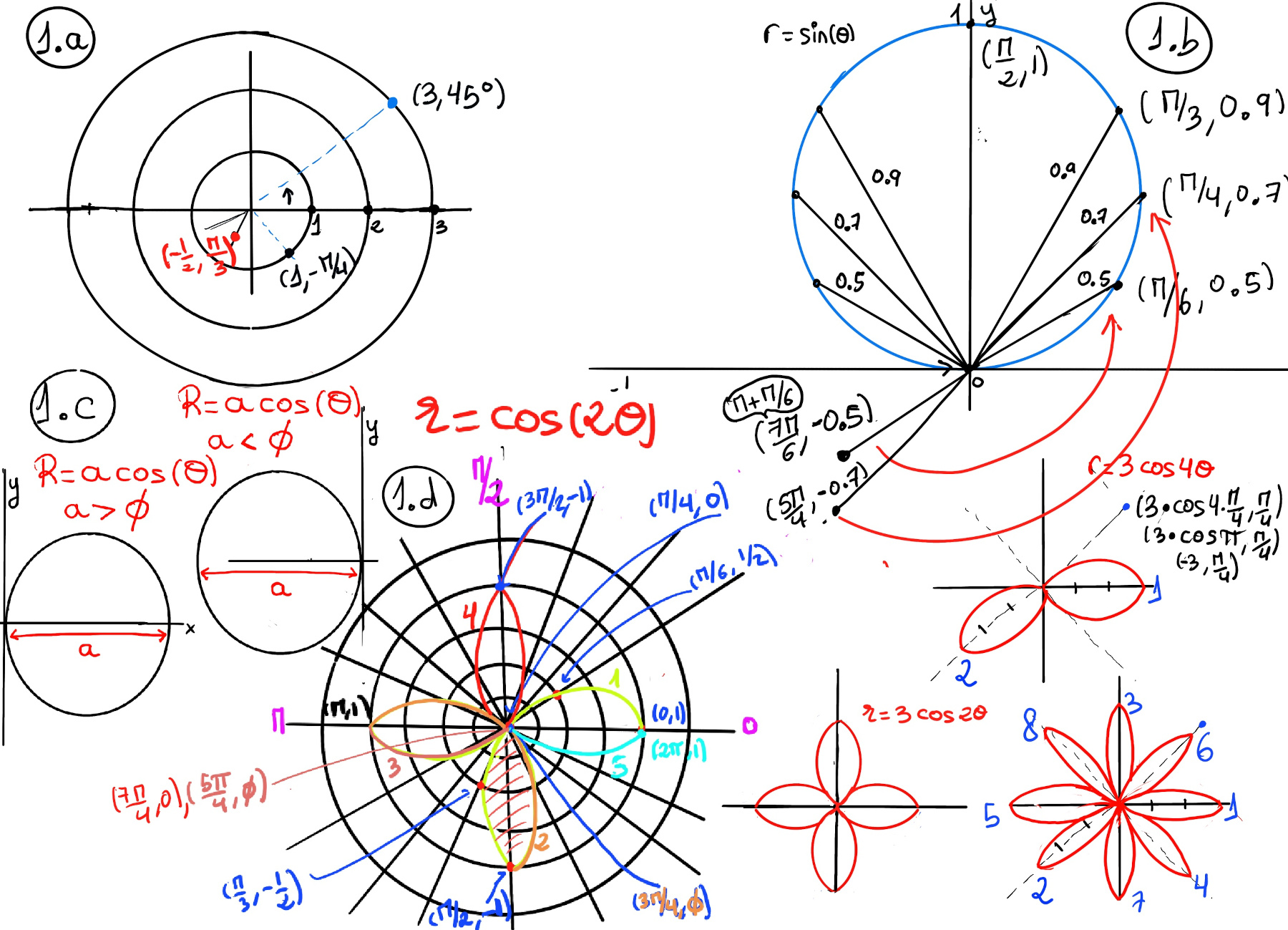
In our case, consider the point (-1⁄2, π⁄3). The negative sign indicates the direction, not the distance, which is always considered positive. x = rcos(θ) = (-1/2)cos(π⁄3) = -1/4, y = rsin(θ) = (-1/2)sin(π⁄3) = -√3/4. The rectangle form is (-1/4, -√3/4). The second representation is (1⁄2, π⁄3 + π).
The point (x,y) = (0, 1) corresponds to (r, θ) = (1, π/2), meaning 1/4 turn counterclockwise from the positive axis. However, we could we could equally well get to this point by a 3/4 turn clockwise, giving (r, θ) = (1, −3π/2). It is also useful to allow negative radius: (−r, θ) means to move out along the line at angle θ, but in the opposite direction from the positive ray, along the ray θ ± π; thus: (−r, θ) = (r, θ ± π).
Let’s consider the polar curve: r = sin(θ). Look along the positive x-axis in direction θ = 0, and draw the origin, r = sin(0) = 0. As you increase θ > 0, turning slowly to the left, you increase the radius as sin(θ) increases (r = sin(π/6) = 0.5, r = sin(π/4) = 0.7, r = sin(π/3) = 0.9). The radius tops out at 1 when θ = π/2 along the positive y-axis; and as you continue to turn, the point comes back in to the origin when θ = π. After that, as you turn toward negative y directions (π ≤ θ ≤ 2π) the radius becomes negative, in fact retracing the original circle (Figure 1.b.).

r = acos(θ) is a circle towards the right (a > 0) or the left (a < 0) where a is the diameter of the circle (Figure 1.c.).
Let’s plot r = 3cos(2θ) and r = 3cos(4θ), r = 3cos(6θ), r = 3cos(8θ) (Figure 1.d), we are going to have a four and eight “leaf roses”. the distance from the origin to the end of the leaf is going to be determined by the constant 3. The number that multiply θ determines how many leafs you have, so we will have roses with 4 and 8 respectively. Besides, r = 3cos(2θ), the first leave for the cosine will be in the positive x direction.

The area, A, of a circle can be found by multiplying Pi (3.14) by the radius squared = πa2. The arc length if the percentage ($\frac{Δθ}{2π}$) of the total area of the circle, so equals ΔA =$\frac{Δθ}{2π}πa^2 =\frac{1}{2}a^2Δθ$, (Figure 1.a)
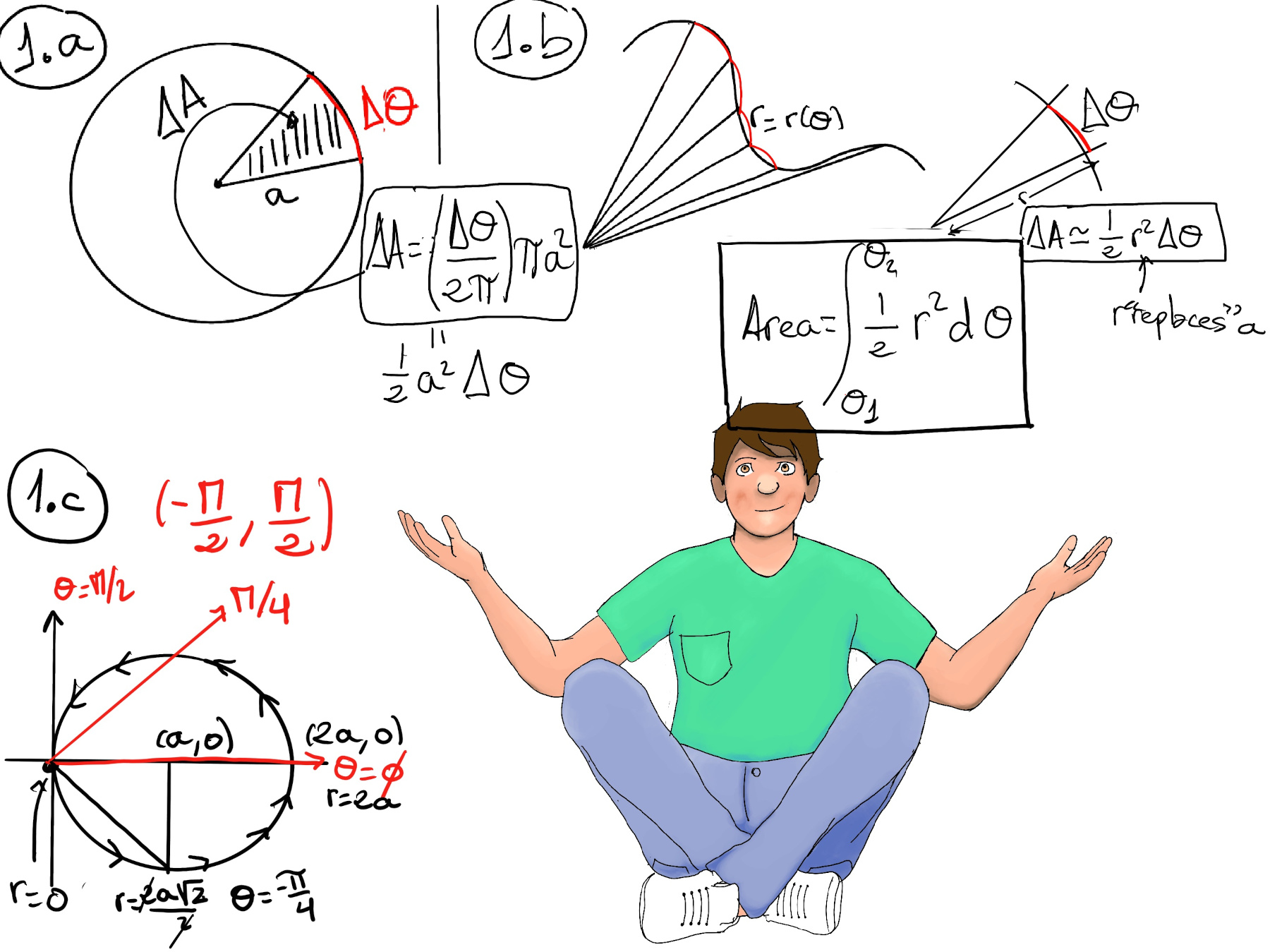
To calculate the area of an area enclosed by a polar curve, the reader should notice that ΔA ≈ $\frac{1}{2}r^2Δθ$, at an infinitesimal scale dA = $\frac{1}{2}r^2dθ$, so the Area = $\int_{θ_1}^{θ_2} \frac{1}{2}r^2dθ$ (Figure 1.b.)
Example, the circle with center (a, 0) and radius a, is described by the polar equation r = 2acos(θ), (x-a)2 + y2 = a2, $\frac{-π}{2}< θ < \frac{π}{2}$ (Notice that cos(±π⁄2) = 0). Area = $\int_{\frac{-π}{2}}^{\frac{π}{2}} \frac{1}{2}(2acos(θ))^2dθ = 2a^2\int_{\frac{-π}{2}}^{\frac{π}{2}} cos^2(θ)dθ = 2a^2\int_{\frac{-π}{2}}^{\frac{π}{2}} \frac{1+cos(2θ)}{2}dθ = a^2(θ +\frac{1}{2}sin(2θ))\bigg|_{\frac{-π}{2}}^{\frac{π}{2}} = a^2(\frac{π}{2}-\frac{-π}{2}) = πa^2,$ aka the area of the circle 😃