
|
 |
 |
|
 |
The heartland of medicine is the human body. It is the science that deals with diseases or illnesses, the best ways to prevent them and the best ways to return to a healthy condition. The human body is an incredible machine. It is a complicated living machine in which various systems work together as a functioning whole.
Cells are the basic building units of life, in other words, all organisms are made of cells. Living organisms are classified as unicellular or multicellular. Unicellular organisms are living things made of a single cell. Some examples of unicellular organisms are amoeba, bacteria, and paramecium.
Multicellular organisms are those that are made up of more than one cell. Life thrives on Earth as plants, animals, and other living things. It is full of multicellular, that is, many-celled organisms.

All cells are divided into two types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are those that do not have a nucleus. They are much smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells. Bacteria and archaea are both prokaryotes. Bacteria come in different shapes and sizes, such as spheres, rod-shaped, and spirals. Bacteria can be found in soil, lakes, rivers, oceans, acidic hot springs, and even radioactive waste.
Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus, which means the cell’s DNA is surrounded by a membrane. They are much larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. Animals, plants, and fungi (yeast and mushrooms) are all eukaryotic organisms.

A group of cells with a specific function is called a tissue. An organ is a collection of tissues that has a specific and important role to play in the human body. Examples of organs are the stomach, heart, lungs, eyes, ears, and brain. An organ system consists of two or more organs working together to perform a specific function.
For example, our digestive system is where we absorb food nutrients and eliminate toxins. Its main organs are: the mouth, stomach, liver, pancreas, small intestine, and large intestine.

The muscular system allows us to move and make facial expressions. We also need it to breathe, digest food, and pump our blood through the circulatory system.

The skeletal system gives us shape, strength to support our body, and protects our delicate and vital internal organs. The skull shields the brain and eyes, the ribcage guards the heart and lungs, and the backbone protects the spinal cord.

The immune system is the body’s defense against infections by microorganisms, such as very small bacteria or viruses, and other invaders. It produces special cells called antibodies to fight off or kill these microorganisms.
The respiratory system is responsible for getting oxygen to our blood and removing carbon dioxide from the body.

The nervous system sends, receives, and processes nerve impulses throughout the body that tell our muscles and organs what to do and how to respond to the environment.
The integumentary system protects our bodies by providing a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. It is comprised of skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands.

There are more organ systems, such as the circulatory system, a network of tubes that transport blood throughout the body; the urinary system helps the body get rid of waste; and the reproductive system, which is essential for the survival of our species.

Our body is an incredible machine that works tirelessly to keep us alive! We need to take good care of it to stay healthy and live longer and better.

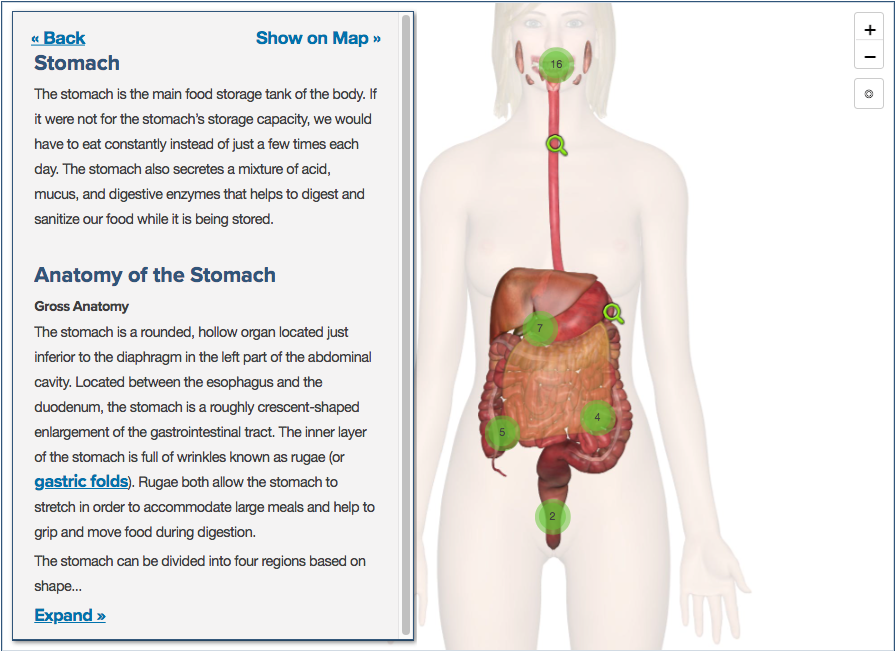

Other resources: TeachMe Anatomy provides students, doctors , and health professionals with the world’s most comprehensive anatomy learning platform. Each page follows a similar pattern: an introduction to the topic, an article, images, quiz, and 3D Body (it is only accessible with the paid premium tier). Essential Anatomy and Complete Anatomy allow you to study human anatomy in an easy and interactive way. However, they are not free.
Advantis Medical. Section Articles, A Pediatric Nurses Guide to the Human Body, and A-School Nurses Guide to Kids Health Wellness and Safety.